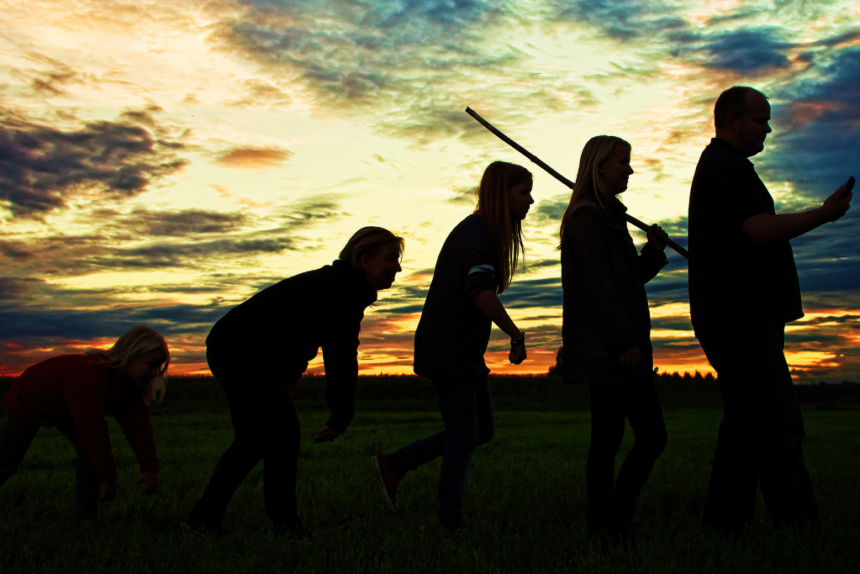
Humans are the predominant species on Gaia, characterised by their remarkable ability to transform their environment, create culture and reflect on their existence. From humble origins to becoming a global force, humans have been on a journey of adaptation, conflict and achievement. This article provides an overview for visitors from other worlds who wish to understand Gaia’s most influential inhabitants.
Humans can perform acts of generosity and compassion, but also of cruelty, destruction and violence at unthinkable levels.
Origins: A species that learns to walk and create
Modern humans (Homo sapiens) emerged approximately 300,000 years ago in Africa. Through a long evolutionary process, they developed abilities that set them apart from other species:
- Fire mastery: This advance made it possible to cook food, keep warm and protect themselves from predators
- Language: The ability to communicate in a complex way facilitated the transmission of knowledge and social organisation.
- Tools: From simple sharpened stones to complex instruments, the use of tools marked their technological advancement
Early civilisations
About 12,000 years ago, with the development of agriculture, humans went from being nomadic hunter-gatherers to establishing permanent settlements. This gave rise to early civilisations in regions such as Mesopotamia, Egypt, the Indus Valley and China. These cultures created writing systems, organised religion and monumental architecture.
Expansion and Cultural Diversity
Over time, humans colonised all of Gaia’s habitable continents, adapting to diverse climates and geographies. This expansion resulted in an impressive cultural and linguistic diversity.

- Religions: Belief systems such as Abrahamic religions, Eastern philosophies and indigenous traditions emerged, guiding humans in their search for purpose and connection to the transcendental.
- Art and science: From cave paintings to the first astronomical observations, humans began to express their creativity and curiosity
Conflicts and alliances
As societies grew, so did conflicts over resources and power. However, these interactions led to cultural exchange, technological innovation, and the formation of alliances that shaped history.
Revolutions: The transformation of society
Over the past 500 years, mankind has experienced revolutions that have drastically changed the way we live:
- Scientific Revolution: In the 17th century, the scientific method enabled advances in astronomy, physics, and medicine, challenging traditional beliefs.
- Industrial Revolution: In the 18th century, the use of machines and fossil fuels transformed production, the economy and social structure, but also initiated an unsustainable dependence on natural resources.
- Digital Revolution: In the 20th century, advances in computer technology connected humans through global networks, changing how they work, communicate, and access knowledge.
Today’s challenges: A planet on the edge
Today, humanity faces global challenges that test its ability to cooperate and adapt:
- Climate change: The impact of their activities on ecosystems and the climate threatens the stability of Gaia
- Social Inequality: While some humans enjoy advanced resources and technologies, many still live in extreme poverty
- Space exploration: In their quest for expansion, humans have begun to explore other planets, but their progress in this area is limited.
Before dealing with them you better prepare yourself, you never know what kind of specimen you’re going to interact with.
Key aspects to understand the human being
For a visitor from other worlds, understanding humans requires observing their contradictions:
- Capacity for good and evil:
- Humans can perform acts of generosity and compassion, but also cruelty, destruction and violence at unthinkable levels. Both of these opposites are as radically present in this species as in any other known species
- Culture as a driver of identity:
- Through their traditions, art and technology, humans try to make sense of their existence
- Resilience and curiosity:
- Despite their challenges, humans have demonstrated a remarkable ability to adapt and overcome adversity

The human paradox: Community and individuality
A distinctive feature of humans is their gregarious tendencies, which have led them to form communities since their earliest days as a species. Humans have thrived on their ability to collaborate in groups, develop complex social networks and establish mutual support systems. From small nomadic tribes to large modern cities, a sense of belonging to a community is fundamental to their emotional and social well-being.
The balance between community and individuality
However, this need to be part of a group contrasts with another equally strong characteristic: their desire for individual freedom and to stand out from the crowd. Humans seek recognition for their achievements, crave autonomy, and often question the norms of the communities to which they belong.
- The search for balance:
- In some cultures, the individual is valued above the community, celebrating creativity, innovation and leadership
- In others, social cohesion is prioritised, where the needs of the group are placed above personal aspirations
- Examples in history:
- Revolutions, such as the independence of various nations and the civil rights movements, were born out of the clash between the desire for individual freedom and the restrictions imposed by social structures
- At the same time, collective advances, such as city building, scientific exploration, or the creation of governance systems, have been made possible by mass collaboration.
A dualism that defines its evolution
This paradox is one of the drivers of human social evolution. On the one hand, their inclination towards community has allowed them to build complex societies and solve problems collectively. On the other, their individual drive has led to the development of revolutionary ideas, sublime art and technologies that have transformed their world.
From an Exogai perspective, this fragile balance between community and individuality is one of the most fascinating characteristics of humans, but also a constant source of internal and external conflict. Will they manage to find a more harmonious balance as they move into the future? Only time will tell.
A complex species with immense potential
Humans are a complex species, with immense potential but also self-inflicted challenges that threaten their survival. For a visitor from another world, understanding humans means accepting their contradictions and observing how they navigate the constant interplay between their successes and their mistakes.
The story of humans on Gaia is one of change, innovation and struggle. Though they have made great strides, their future depends on their ability to balance their progress with the preservation of their world. For those arriving on Gaia for the first time, humans are both a fascination and a warning: before dealing with them you had better prepare yourself, you never know what kind of specimen you will be interacting with.





